Introduction to the stored program concept
John von Neumann first presented the concept in the late 1940s. He suggested that a programme be electronically stored in a memory device in binary-number format so that the computer may alter the instructions based on intermediate computing results.
The stored program concept is a fundamental idea in computer science that refers to the organization of instructions and data within a computer's memory. It is a key principle behind the structure of modern computers and plays an important part in their ability to perform a wide range of tasks.
In a system, based on the stored program concept, both program instructions and data are stored in the computer's memory in a binary format. This means that the instructions that control the computer's operations are represented as binary code and are treated like any other data. This is in contrast with earlier computing models where the program and data were stored separately.Read more
The key components of the stored program concept include:
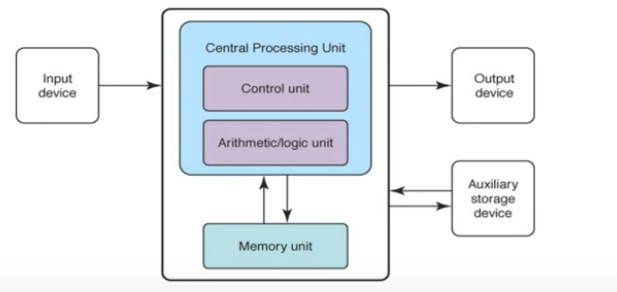
Memory: A unified memory system that stores both program instructions and data. This memory is accessible by the central processing unit (CPU), which can fetch and execute instructions from it.
Instructions as Data: Program instructions are stored in the same memory as data, and both are represented in binary form. This allows for flexibility, as the same memory locations can be used for both program instructions and data.
Sequential Execution: The CPU fetches instructions from memory one at a time and executes them sequentially. This sequential execution of instructions forms the basis for the logical flow of a computer program.
Control Flow: The program instructions include control flow instructions, such as branches and jumps, which enable the computer to make decisions and change the order of instruction execution based on conditions.
Stored Program Principle: The concept that a computer can be designed to be versatile and programmable by allowing the user to load different programs into memory. This provides a foundation for the development of a wide variety of applications without the need to modify the computer's hardware.
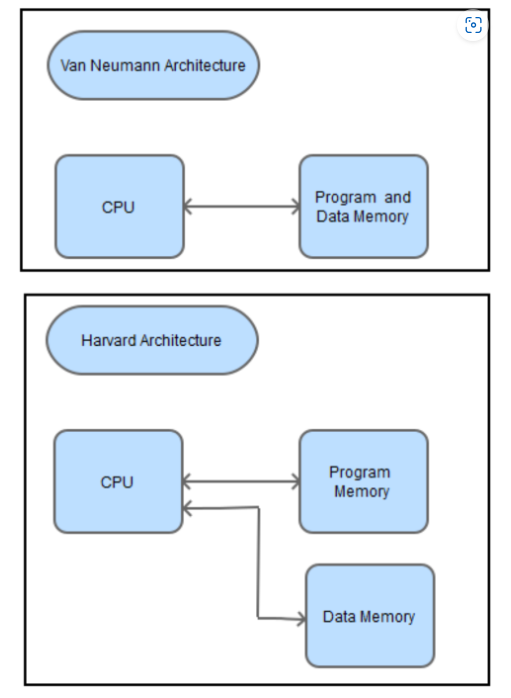
Difference between von Neumann and Harvard architectures
Von Neumann vs. Harvard Architecture
| VON NEUMANN ARCHITECTURE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| It is ancient computer architecture based on stored program computer concept. | Same physical memory address is used for instructions and data. | There is a common bus for data and instruction transfer. | Two clock cycles are required to execute a single instruction. | It is cheaper in cost. | CPU cannot access instructions and read/write at the same time. | It is used in personal computers and small computers. |
| HARVARD ARCHITECTURE | ||||||
| It is modern computer architecture based on the Harvard Mark I relay-based model. | Separate physical memory addresses are used for instructions and data. | Separate buses are used for transferring data and instructions. | An instruction is executed in a single cycle. | It is costlier than Von Neumann Architecture. | CPU can access instructions and read/write at the same time. | It is used in microcontrollers and signal processing. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Harvard Architecture
Harvard Architecture Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Due to instructions and data being transferred in different buses, there is a smaller chance of data corruption. | The memory dedicated to each (data and instructions) must be balanced by the manufacturer. If there is free memory in data memory, it cannot be used for instructions and vice versa. |
| Instructions and data can be accessed the same way. | This advantage results in a more complex architecture, as it requires two buses. This makes manufacturing time-consuming and increases system costs. |
| Harvard architecture offers high performance, allowing simultaneous flow of data and instructions kept in separate memory via separate buses. | Despite high performance, Harvard architecture is complex, especially for mainboard manufacturers to implement. |
| Greater memory bandwidth that is more predictable due to the architecture having separate memory for instructions and data. | To achieve the advantage of separate buses, Harvard architecture requires a control unit for two buses, increasing complexity and development difficulty, ultimately raising the system's price. |
Von Neumann Architecture Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Unified memory simplifies the design and makes it more flexible for various applications. | Sequential execution may result in slower performance for certain tasks that could benefit from parallel processing. |
| Instructions and data share the same memory, reducing the need for separate memory units. | Potential bottlenecks occur as the CPU has to alternate between fetching instructions and accessing data. |
| Cost-effective design due to the use of a single shared memory space for instructions and data. | Limited parallelism can impact overall performance, especially in modern computing environments. |
| Flexibility in modifying programs during runtime as both instructions and data are stored in the same memory. | Not well-suited for tasks that require simultaneous access to large amounts of data and instructions.Read more |
